Calculate the Kaplan-Meier estimator and the Aalen-Johansen estimator
Source:R/cifcurve.R
cifcurve.RdCore estimation routine that computes a survfit-compatible object
from a formula + data interface (Event() or survival::Surv() on
the LHS, and a stratification variable on the RHS if necessary).
The back-end C++ routine supports both weighted and stratified data. Use this
when you want numbers only (e.g. estimates, SEs, CIs and influence functions)
and will plot it yourself.
Usage
cifcurve(
formula,
data,
weights = NULL,
subset.condition = NULL,
na.action = na.omit,
outcome.type = c("survival", "competing-risk"),
code.event1 = 1,
code.event2 = 2,
code.censoring = 0,
error = NULL,
conf.type = "arcsine-square root",
conf.int = 0.95,
report.influence.function = FALSE,
report.survfit.std.err = FALSE,
engine = "calculateAJ_Rcpp",
prob.bound = 1e-07
)Arguments
- formula
A model formula specifying the time-to-event outcome on the LHS (typically
Event(time, status)orsurvival::Surv(time, status)) and, optionally, a stratification variable on the RHS. Unlikecifplot(), this function does not accept a fitted survfit object.- data
A data frame containing variables in the formula.
- weights
Optional name of the weight variable in
data. Weights must be nonnegative.- subset.condition
Optional character string giving a logical condition to subset
data(defaultNULL).- na.action
A function specifying the action to take on missing values (default
na.omit).- outcome.type
Character string specifying the type of time-to-event outcome. One of
"survival"(Kaplan-Meier) or"competing-risk"(Aalen-Johansen). IfNULL(default), the function automatically infers the outcome type from the data: if the event variable has more than two unique levels,"competing-risk"is assumed; otherwise,"survival"is used. You can also use abbreviations such as"S"or"C". Mixed or ambiguous inputs (e.g.,c("S", "C")) trigger automatic detection based on the event coding.- code.event1
Integer code of the event of interest (default
1).- code.event2
Integer code of the competing risk (default
2).- code.censoring
Integer code of censoring (default
0).- error
Character string specifying the method for SEs and CIs used internally. For
"survival"without weights, choose one of"greenwood"(default),"tsiatis", or"if". For"competing-risk"without weights, choose one of"delta"(default),"aalen", or"if". SEs and CIs based on influence functions ("if") is recommended for weighted analysis.- conf.type
Character specifying the method of transformation for CIs used internally (default
arcsine-square root).- conf.int
Numeric two-sided level of CIs (default
0.95).- report.influence.function
Logical. When
TRUEandengine = "calculateAJ_Rcpp", the influence function is also computed and returned (defaultFALSE).- report.survfit.std.err
Logical. If
TRUE, report SE on the log-survival scale (survfit's convention). Otherwise SE is on the probability scale.- engine
Character. One of
"auto","calculateKM", or"calculateAJ_Rcpp"(default"calculateAJ_Rcpp").- prob.bound
Numeric lower bound used to internally truncate probabilities away from 0 and 1 (default
1e-7).
Value
A "survfit" object. For outcome.type="survival", $surv is the survival function.
For outcome.type="competing-risk", $surv equals 1 - CIF for code.event1.
SE and CIs are provided per error, conf.type and conf.int.
This enables an independent use of standard methods for survfit such as:
summary(): time-by-time estimates with SEs and CIsplot(): base R stepwise survival/CIF curvesmean(): restricted mean survival estimates with CIsquantile(): quantile estimates with CIs
Note that $n.risk, $n.event, and $n.censor are rounded up to the nearest integer
regardless of whether the data is weighted or not.
Some methods (e.g. residuals.survfit) may not be supported.
Details
Typical use cases
When
outcome.type = "survival", this is a thin wrapper around the KM estimator with the chosen variance / CI transformation.When
outcome.type = "competing-risk", this computes the AJ estimator of CIF forcode.event1. The returned$survis 1 - CIF, i.e. in the format that ggsurvfit expects.Use
cifplot()if you want to go straight to a figure; usecifcurve()if you only want the numbers.
Standard error and confidence intervals
| Argument | Description | Default |
error | SE for KM: "greenwood", "tsiatis", "if". For CIF: "aalen", "delta", "if". | "greenwood", "delta" or "if" |
conf.type | Transformation for CIs: "plain", "log", "log-log", "arcsin", "logit", or "none". | "arcsin" |
conf.int | Two-sided CI level. | 0.95 |
See also
polyreg() for log-odds product modeling of CIFs; cifplot() for display of a CIF; cifpanel() for display of multiple CIFs; ggsurvfit::ggsurvfit, patchwork::patchwork and modelsummary::modelsummary for display helpers.
Examples
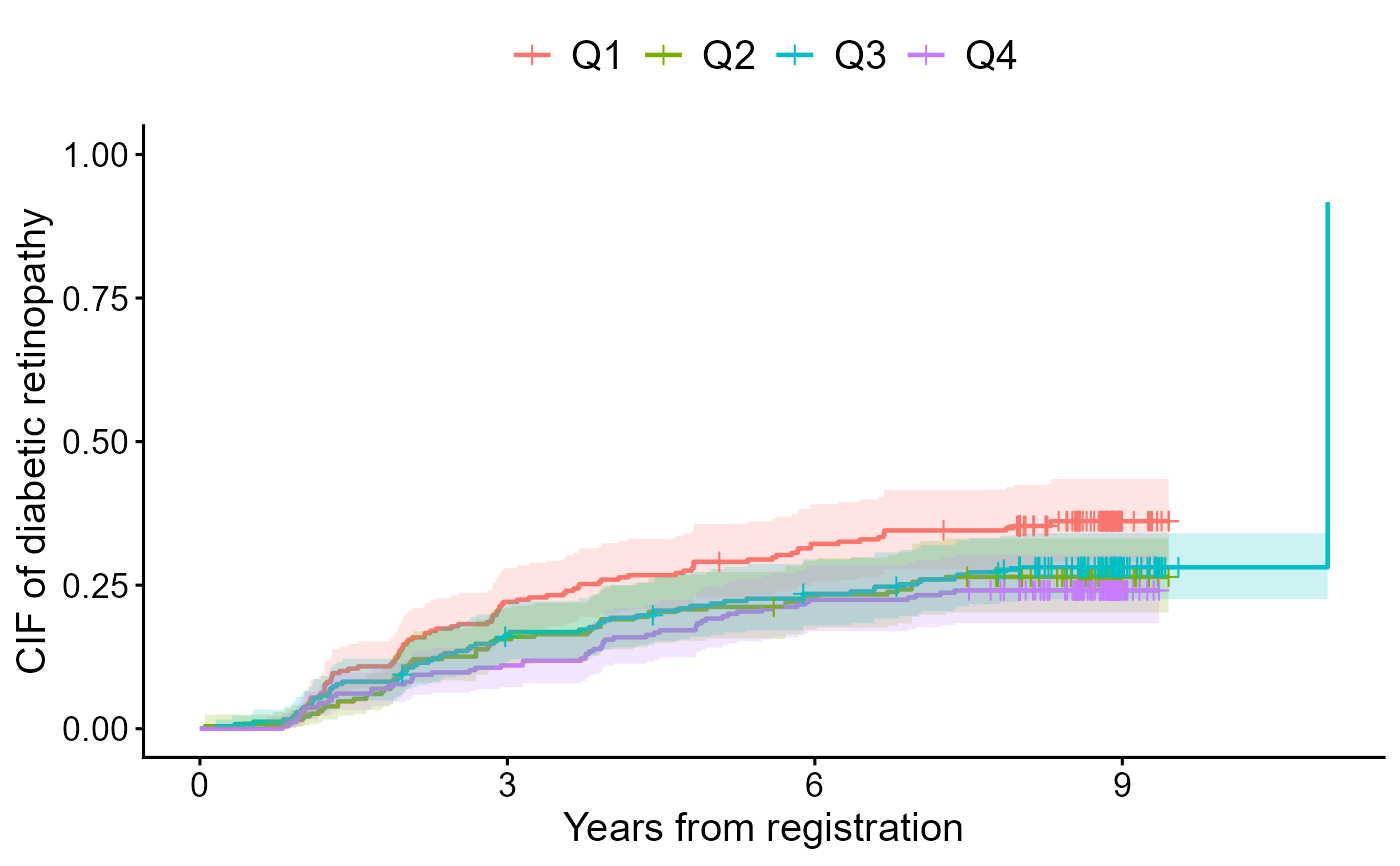
data(diabetes.complications)
output1 <- cifcurve(Event(t,epsilon) ~ fruitq,
data = diabetes.complications,
outcome.type="competing-risk")
cifplot(output1,
outcome.type = "competing-risk",
type.y = "risk",
add.risktable = FALSE,
label.y = "CIF of diabetic retinopathy",
label.x = "Years from registration")